A rare case of Hyperphosphatemic Tumoral Calcinosis in a 13 year old Nigerian boy
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 15 May 2023
Authors
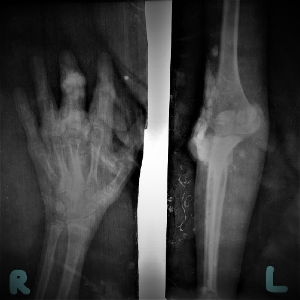
Tumoral calcinosis is a rare disorder that presents with ectopic calcifications deposited at different periarticular soft tissue regions of the body- mostly hips, elbows and shoulders. It results from a relative deficiency of, or resistance to, the phosphate-regulating hormone - Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23), due to gene mutations, causing hyperphosphatemia. We describe this condition in a 13 year old, Nigerian boy who presented with a 7 year history of multiple body swellings of firm to hard consistency. Laboratory investigations showed hyperphosphatemia with normal serum calcium, vitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels. Radiological and histological findings were consistent with tumoral calcinosis. Having had two previous surgeries to remove the lesions, he was now commenced on low phosphate diet and phosphate binders. It is important to differentiate tumoral calcinosis from other causes of pathological calcification using clinical and laboratory findings especially in environments where molecular genetic testing is not readily available.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






